Arthrosis is a disease characterized by gradual destruction of the joint in tissues due to the development of dystrophic changes.WHO says every tenth inhabitants of the planet face this problem.After 50 years, the risk of the disease is about 30%and reaches 80-90%70 years.
General information
Arthrosis is a chronic, long -term process that not only affects the joints.During the progress, the dyspic and degenerative changes are also wonderful for the additional device.During the process, the patient should be faced with inflammation of the cartilage and bone tissue, the joint capsule and the periosemantial bag, as well as the contact with muscles, ligaments and subcutaneous tissues.
Regardless of the localization, the pathological process goes according to a single scheme.First, in the thickness of the tissue, the balance between the growth process and destruction of the cartilage is disturbed, and the balance changes to the benefit of dystrophy and reverse development (degeneration).At this time, there are invisible changes in the micro -structure of the cartilage, leading to thinning and cracks.
As the disease progresses, the joint loses its elasticity and becomes thicker.This reduces the ability to deprecate, and the rate of tissue damage is constantly increasing due to vibration and microtrauma during movements.The thinning of the cartilage provokes the active growth of bone structures, which results in spikes and ledges appear on the smooth surface of the joint - osteoarthrosis.Movements are increasingly limited and painful.The muscles surrounding the affected area develop cramps, which exacerbates the pain and deforms the limb.
The stages of illness
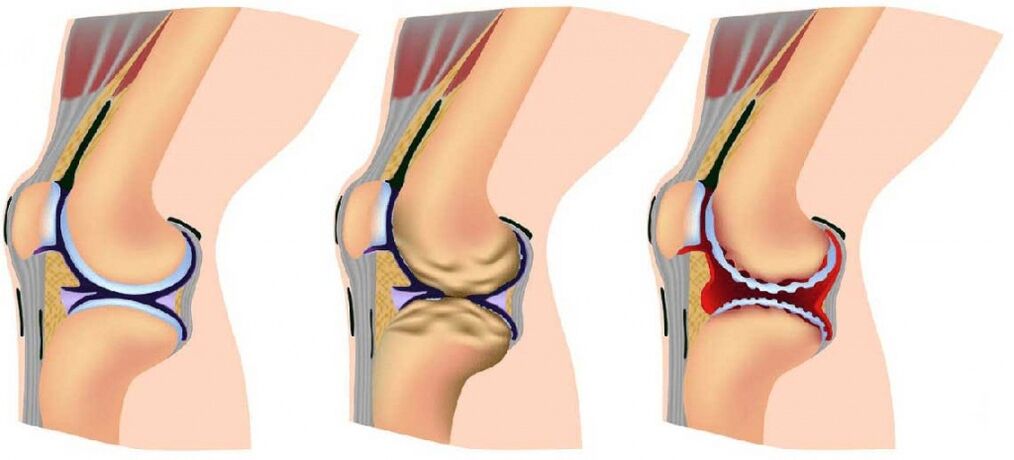
The arthrosis of the joints gradually develops and during the process of three consecutive stages that determine the severity of the disease:
- Section 1: Pathology is not detected by an X -ray or ultrasound, but the destruction processes have already been launched;The composition of the joint fluid changes, which results in tissues less than nourishing creatures and becomes more sensitive;Increased burden on the area of damage causes inflammation (joint inflammation) and pain;
- Stage 2 is characterized by active destruction of the cartilage tissue and bone spikes and growths appear on the edges of the joint platform (the surface of the surfaces);At this time, the pain is familiar and the inflammatory processes are stronger or weaker;Cramps related to muscle joints can be observed regularly;
- Section 3: The areas of destruction affect the almost entire surface of the cartilage, the common platform is deformed, the damaged limb is different from the axis;The amount of movements decreases, the tapes are weakened and short.
Some experts distinguish between the development of arthrosis IV.This is characterized by almost complete mobility of the joint.
Type
Depending on the cause of the disease, primary and secondary arthrosis are distinguished.In the first case, the pathology is independently caused by the background of the comprehensive effects of prone factors.The secondary form is the result of other diseases and is divided into the following groups:
- Damage to joints due to metabolic disorders or endocrine diseases (gout, diabetes mellitus, acromegaly, hyperparatheroidism);
- Destruction related to congenital pathologies (pedget -blood, congenital lips dislocation, skoliosis, hemophilia, etc.);
- Post -trauma arthrosis, which is due to fractures, cracks, necrotic processes or surgical operations and the characteristics of the profession.
Mostly classification of osteoarthritis, depending on the localization of the pathological process:
- Gonarthrosis: the lesion of the knee, one of which is the pallet -pemoral arthrosis - the destruction of the joint between the femur and the patella;
- Arthrosis of the ankle joint: occurs in the background of heavy load and frequent injuries;
- The leg joints are joint joint: the thumb is most often suffered from the foot intersection;Defeat develops in the background of gout or valgus deformation;
- Shoulder arthrosis is characterized by shoulder damage and is often found in a young age the background of increased physical activity (movers, athletes, builders);
- Coksartrosis: Damage to the hip joint;It may be both a common cause of disability in both people over 50;
- Vertebrae arthrosis: destruction of cartilage discs between the vertebrae, most often the cervix and lumbar spine;
- Brush joints Arthrosis: Fingers are most commonly affected, pathologies are particularly sensitive to menopause women;
- Temporomandibular joint arthrosis: this is quite rare, most often due to bite disorders or chronic inflammation due to inadequate prosthetics;
- Arthrosis of the elbow joint: a rare form of the disease, which is most often associated with injuries in this area.
Causes of development
The main factor in the development of arthrosis is the difference between the test and the joint ability of the joint to withstand this load.Acute or chronic, this process will inevitably lead to destruction of tissues.
A list of reasons that increase the risk of localization arthrosis:
- heredity;
- endocrine pathology (diabetes);
- Joints of the joint device: crushing, dislocations, fractures or bones in the joint bag, complete or partial fracture of ligaments penetrating into the wounds;
- Regular increased joint load related to the profession;
- obesity;
- hypothermia;
- Transferred inflammatory arthritis: acute arthritis, tuberculosis, etc.;
- blood diseases in which the joint often occurs (hemophilia);
- sharp changes in the hormonal background (pregnancy, menopause);
- Local circulatory disorders are atherosclerosis, varicose veins, thromboflebitis, etc.
- autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, etc.);
- Connective tissue dyplasia (congenital pathology, accompanied, including excessive mobility of the joints);
- Congenital pathologies of the muscle system (flat legs, dysplasia or congenital dislocation of the hip joint, etc.);
- Age over 45-50 years (risk increase results in a decrease in collagen synthesis);
- osteoporosis (bone vacuum);
- Chronic intoxication of the body (including salts of heavy metals, drugs, alcohol);
- Surgical interventions on joints.
Symptoms
Joint symptoms are virtually independent of its cause and localization, as joint changes occur according to the same scenario.The disease gradually develops and is already reflected when the cartilage is quite severely injured.
One of the first signs of dysfunction is the crisis in the problem area during movement.Most often it occurs when the knee or shoulder is damaged.At the same time, people may be slightly reduced, for example in the morning.
When asked which symptoms occurred during arthrosis, most patients first call pain.At first, insignificant and weak, gradually strengthens the strength, preventing it from moving normally.Depending on the stage and localization of the pathology, one may feel:
- Starting pains: during the first movements they occur after the joint inactivity of the joint and are associated with the formation from the destroyed material on the cartilage surface of the thin layer;After work begins, the film shifts and the discomfort disappears;
- Pain extended with extended physical effort (standing, walking, running, etc.): appears due to a reduction in the shock of the joint;
- Weather pain: low temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure changes;
- Night pain: associated with venous stagnation and increased blood pressure within the bones;
- Composition: A sharp, severe pain associated with the cartilage or bone in the joint cavity.
When arthrosis develops, the symptoms become more noticeable, and the patient takes into account the following symptoms:
- an increase in morning stiffness;
- strengthening and increasing the duration of pain;
- decrease in mobility;
- joint deformation due to bone growth;
- Deformation of bones and surrounding tissues: The process is well detected on the limbs and fingers of the hands, which are noticeably curved.
When the inflammation is recorded, the affected area becomes swollen, blushed and hot.The pressure causes a sudden increase in pain.

Analysis and diagnostics
Diagnosis of arthrosis is involved in the orthopedic doctor.He conducts a detailed survey of the patient to identify complaints and anamithesis.The physician in detail the speed of the appearance and development of the first signs, the presence of injuries and diseases and similar problems in relatives.
The general blood test allows you to identify the inflammatory process, which is often accompanied by arthrosis.
The main way of diagnosis is radiography.The following signs are clearly displayed in the picture:
- narrowing of the joint gap;
- Changing the outlines of contact bones;
- disturbed bone structure in the affected area;
- bone growth (osteophytes);
- curvature of the limb or finger shaft;
- Subluxation of the joint.
They can be written for more detailed diagnostics:
- Computer tomography (CT);
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- Ultrasound of the joint;
- arthroscopy (internal examination of the joint cavity with a camera introduced with a small punch);
- Scintigraphy (assessment of the condition of bones and metabolism with the introduction of radiopharmaceous drugs).
In the event of a secondary nature of the disease, the appropriate tests and consultations of narrow professionals are prescribed.
Treatment of joint treatment of joints
Choosing a methodology for joint treatment of joints depends on the cause, stage and symptoms of the disease.They are in the doctors' arsenal:
- drugs;
- no -drog treatment;
- Surgical methods.
In addition, the patient should strictly adhere to the diet and adjust the lifestyle to minimize further damage to the joints.
Drug treatment
The appointment of medicines for arthrosis is two main goals:
- removal of pain and inflammation;
- The restoration of cartilage tissue, or at least stops further degeneration.
Different types of drugs are used to facilitate the patient's condition:
- Non -steroid anti -inflammatory drugs in the form of tablets, injections, ointments or candles;They relieve pain and inflammation;
- Hormones (corticosteroids): in severe pain and most often directly into the joint cavity;
- Other analgesics such as inhibition effect: help reduce the level of pain by relaxing the muscles;
It is important to note that all types of painkillers are only used to facilitate the patient's condition.They do not affect the condition of the cartilage and accelerate destruction for a longer period of time and cause severe side effects.
The main preparation for the recovery of joints today is Chondroprotectors.They contribute to the saturation of cartilage nutrients, stop the memorial and begin cell growth processes.The devices have only an effect on the early and average stages of the disease and are subject to regular long -term use.
In tissues and anti -mesh, microcirculation enhancements promote the effects of chondroprotectors.The former provides good care for the affected area with oxygen and nutrients, and the latter slows down the processes of tissue destruction.
Specific drugs, dosage and the choice of administration are related to the doctor.
No -drog treatment
Nem -drog treatment includes the following methods:
- physiotherapy:
- Shock wave therapy: destroys bones growth and stimulates blood circulation due to the effect of ultrasound;
- Automated electromicostimulation: exposure to electrical impulses to stimulate muscles;
- Ultraphonophoresis: the effect of ultrasound using drugs;
- Ozone therapy: introduction of a special gas mixture into the joint capsule;
- physiotherapy physical education;
- Mechanotherapy: using exercise therapy with simulators;
- Common traffic to reduce load;
- massage.
Surgery
Most often, the surgeon needs help in severe stages of the disease.Depending on the localization of the pathological process and the degree of lesion, it is prescribed:
- Stabbing: Punction of the joint by removing some of the liquid and indicating the administration of the drugs;
- Corrective osteotomy: Removal of a part of the bone followed by anching from another angle to remove the load from the joint;
- Endoprosttetics: Replacing the injured joint with prosthesis;It is used in extremely neglected cases.
Arthrosis in children
Arthrosis is considered to be a disease of the elderly, but can also be found in children.The most common reason for pathology:
- Congenital pathology of connective tissue;
- serious injuries;
- heredity;
- Metabolic disorders and the work of the glands of the internal secretion;
- orthopedic disorders (flat foot, skoliosis, etc.);
- overweight.
Children's joint joint symptoms are rarely accompanied by: pain hurts and virtually no stiffness and restriction of function.Monotetic changes are detected during an X -try, MRI and ultrasound.During treatment, the same products are used as adults.Maximum attention is paid to practicing treatment and physiotherapy because they are particularly effective in young people.Without treatment, the disease will sooner or later cross the advanced stage with a complete loss of mobility.
Diet
Diet is one of the most important factors in the treatment of arthrosis.In the presence of overweight, it should be reduced to reduce the load on joints.In this case, a balanced diet is prescribed with a lack of calories.Regardless of body weight index, doctors leave it completely:
- fast carbohydrates (sugar, desserts, flour);
- alcohol;
- spices;
- legumes;
- strong tea and coffee;
- Too fatty and sharp foods.
The canned and offal cannot be excluded, but significantly limited, as well as salt.The ideal nutrition of osteoarthritis includes the following:
- Low fatty meat types;
- fish and seafood;
- egg;
- dairy products;
- linseed and olive vegetable oils;
- vegetables and fruits, large amounts of green;
- Moderate cereals, dough of hard pasta dough;
- Products with high collagen content (jelly, casting, jelly).
Prevention
Arthrosis is more easily warned than treated.It is recommended to maintain joint health for many years:
- lead an active lifestyle;
- Train and visit the pool regularly;
- Eat properly, use sufficient omega-3 and collagen;
- prevents BMI from exceeding;
- Wear comfortable shoes.
If the disease is diagnosed at an early stage, it is recommended to go regularly for SPA treatment and exclude professional risk factors: long-term stay on the legs, lifting severity, vibration.
Consequences and complications
Arthrosis progresses very slowly.When the doctor's prescription is done, power slows down significantly, which allows you to maintain joint mobility for a long time.The irreversible consequences develop without treatment:
- pronounced joint deformation;
- decreases to the total loss of mobility (ankylosis);
- Shortening of the limb (injury to knee or femoral bone);
- Deformation of bones, curvature of the limbs and fingers.
Forecast
The prognosis of arthrosis depends on the form, degree and quality of treatment.Pathology is one of the common causes of disability and, in advanced cases, the ability of movement and self -service.In severe forms of knee and hip joint damage, the patient receives the first or second disability group (depending on the stage and the amount of damage).